본 게시글의 원문은 Yann Debray의 MATLAB with Python Book 입니다. 해당 책은 MIT 라이센스를 따르기 때문에 개인적으로 번역하여 재배포 합니다. 본 포스팅에는 추후 유료 수익을 위한 광고가 부착될 수도 있습니다.
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2023 Yann Debray
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
본 게시물에서 활용된 소스 코드들은 모두 Yann Debray의 GitHub Repo에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
2.1. 파이썬을 MATLAB에서 호출하기
Heather는 weather.py라는 모듈을 만들었습니다. 이 모듈은 웹 서비스에서 데이터를 읽고 반환된 JSON 데이터를 구문 분석합니다. 물론 MATLAB에서도 이 작업을 수행할 수 있지만, 데이터에 접근하는 예제로 이 모듈을 사용해보겠습니다.
2.1.1. 파이썬 설치 확인
먼저 pyenv 명령을 사용하여 Python 환경에 연결합니다. MATLAB 및 Python 설정에 대한 자세한 내용은 다음 장을 참조하십시오. MATLAB은 기본 Python, 설치한 패키지 및 사용자 고유의 Python 코드에서 파이썬 함수를 호출하고 파이썬 개체를 생성할 수 있습니다.
pyenv % MATLAB 버전 R2019b 이전에는 pyversion을 사용하세요.
ans =
PythonEnvironment with properties:
Version: "3.10"
Executable: "C:\Users\ydebray\AppData\Local\WPy64-31040\python-3.10.4.amd64\python.exe"
Library: "C:\Users\ydebray\AppData\Local\WPy64-31040\python-3.10.4.amd64\python310.dll"
Home: "C:\Users\ydebray\AppData\Local\WPy64-31040\python-3.10.4.amd64"
Status: NotLoaded
ExecutionMode: OutOfProcess
2.1.2. 파이썬 사용자 정의 함수 MATLAB에서 호출하기
이제 동료의 날씨 모듈을 어떻게 사용하는지 알아보겠습니다. 먼저 오늘 날짜의 데이터를 가져오겠습니다. 날씨 모듈의 get_current_weather 함수는 Json 형식으로 현재 날씨 상황을 가져옵니다. 그런 다음 parse_current_json 함수는 이 데이터를 파이썬 딕셔너리 형식으로 반환합니다.
jsonData = py.weather.get_current_weather("London","UK",appid,api='samples')
jsonData =
Python dict with no properties.
{'coord': {'lon': -0.13, 'lat': 51.51}, 'weather': [{'id': 300, 'main': 'Drizzle', 'description': 'light intensity drizzle', 'icon': '09d'}], 'base': 'stations', 'main': {'temp': 280.32, 'pressure': 1012, 'humidity': 81, 'temp_min': 279.15, 'temp_max': 281.15}, 'visibility': 10000, 'wind': {'speed': 4.1, 'deg': 80}, 'clouds': {'all': 90}, 'dt': 1485789600, 'sys': {'type': 1, 'id': 5091, 'message': 0.0103, 'country': 'GB', 'sunrise': 1485762037, 'sunset': 1485794875}, 'id': 2643743, 'name': 'London', 'cod': 200}
weatherData = py.weather.parse_current_json(jsonData)
weatherData =
Python dict with no properties.
{'temp': 280.32, 'pressure': 1012, 'humidity': 81, 'temp_min': 279.15, 'temp_max': 281.15, 'speed': 4.1, 'deg': 80, 'lon': -0.13, 'lat': 51.51, 'city': 'London', 'current_time': '2023-03-15 16:04:38.427888'}
2.1.3. 파이썬 데이터를 MATLAB 데이터로 변환하기
이제 Python 딕셔너리를 MATLAB 구조체로 변환해보겠습니다.
data = struct(weatherData)
data =
temp: 280.3200
pressure: [1x1 py.int]
humidity: [1x1 py.int]
temp_min: 279.1500
temp_max: 281.1500
speed: 4.1000
deg: [1x1 py.int]
lon: -0.1300
lat: 51.5100
city: [1x6 py.str]
current_time: [1x26 py.str]
대부분의 데이터는 자동으로 변환됩니다. 몇 가지 필드만이 명확한 동등한 항목을 찾지 못했습니다.
pressure와humidity는 MATLAB에서py.int객체로 남습니다.city와current_time은 MATLAB에서py.str객체로 남습니다.
우리는 double, string 및 datetime과 같은 표준 MATLAB 함수를 사용하여 명시적으로 변환할 수 있습니다.
data.pressure = double(data.pressure);
data.humidity = double(data.humidity);
data.deg = double(data.deg);
data.city = string(data.city);
data.current_time = datetime(string(data.current_time))
data =
temp: 280.3200
pressure: 1012
humidity: 81
temp_min: 279.1500
temp_max: 281.1500
speed: 4.1000
deg: 80
lon: -0.1300
lat: 51.5100
city: "London"
current_time: 15-Mar-2023 16:04:38
2.1.4. 파이썬 리스트를 MATLAB 행렬로 변환하기
이제 get_forecast 함수를 호출해보겠습니다. 이 함수는 다음 몇 일 동안 예측된 날씨 조건 시리즈를 반환합니다. 구조체의 필드는 Python 리스트로 반환됩니다.
jsonData = py.weather.get_forecast('Muenchen','DE',appid,api='samples');
forecastData = py.weather.parse_forecast_json(jsonData);
forecast = struct(forecastData)
forecast =
current_time: [1x36 py.list]
temp: [1x36 py.list]
deg: [1x36 py.list]
speed: [1x36 py.list]
humidity: [1x36 py.list]
pressure: [1x36 py.list]
숫자 데이터만 포함하는 리스트는 double 형식으로 변환될 수 있습니다 (MATLAB R2022a부터):
forecast.temp = double(forecast.temp) - 273.15; % from Kelvin to Celsius
forecast.temp
ans = 1x36
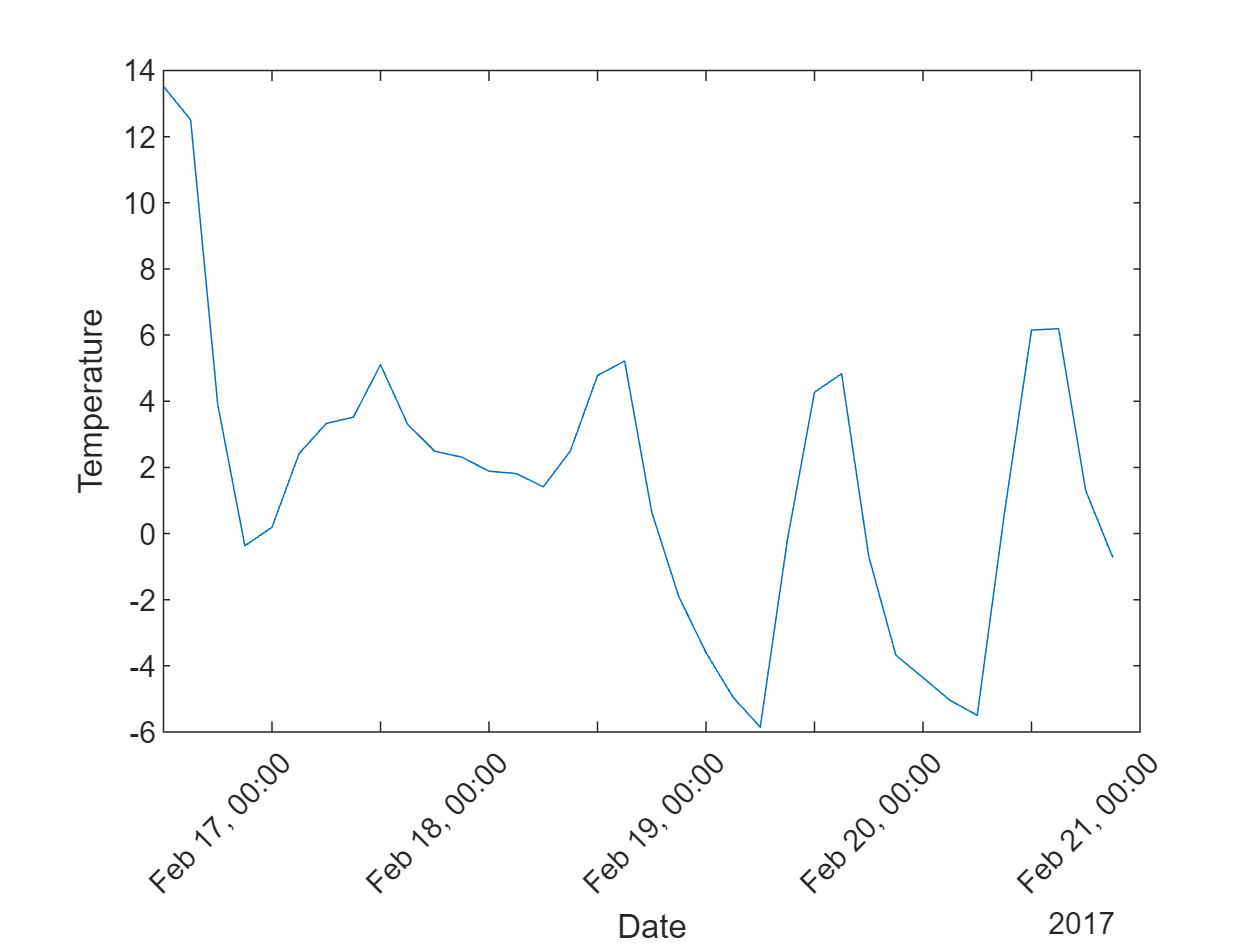
13.5200 12.5100 3.9000 -0.3700 0.1910 2.4180 3.3280 3.5200 5.1030 3.3050 2.4890 2.3090 1.8850 1.8150 1.4120 2.4980 4.7770 5.2170 0.6470 -1.9110 -3.5970 -4.9520 -5.8550 -0.1940 4.2720 4.8340 -0.6910 -3.6770 -4.3570 -5.0440 -5.4950 0.6000 6.1520 6.1930 1.2930 -0.7260
텍스트를 포함하는 리스트는 문자열로 변환되며, datetime과 같은 특정 데이터 유형으로 더 처리될 수 있습니다.
forecast.current_time = string(forecast.current_time);
forecast.current_time = datetime(forecast.current_time);
forecast.current_time
ans = 1x36 datetime
16-Feb-2017 12:00:0016-Feb-2017 15:00:0016-Feb-2017 18:00:0016-Feb-2017 21:00:0017-Feb-2017 00:00:0017-Feb-2017 03:00:0017-Feb-2017 06:00:0017-Feb-2017 09:00:0017-Feb-2017 12:00:0017-Feb-2017 15:00:0017-Feb-2017 18:00:0017-Feb-2017 21:00:0018-Feb-2017 00:00:0018-Feb-2017 03:00:0018-Feb-2017 06:00:0018-Feb-2017 09:00:0018-Feb-2017 12:00:0018-Feb-2017 15:00:0018-Feb-2017 18:00:0018-Feb-2017 21:00:0019-Feb-2017 00:00:0019-Feb-2017 03:00:0019-Feb-2017 06:00:0019-Feb-2017 09:00:0019-Feb-2017 12:00:0019-Feb-2017 15:00:0019-Feb-2017 18:00:0019-Feb-2017 21:00:0020-Feb-2017 00:00:0020-Feb-2017 03:00:00
Section 4.7에서 파이썬과 MATLAB 간의 데이터 변환에 대해 더 자세하게 확인할 수 있습니다.
2.1.5. Python 데이터를 가져와 MATLAB에서 그래프로 탐색하기
plot(forecast.current_time,forecast.temp)
xtickangle(45)
xlabel('Date')
ylabel('Temperature')
2.1.6. MATLAB에서 머신 러닝 모델 호출하기
이제 우리가 일부 역사적 데이터를 사용하여 날씨 조건 세트를 가져와 대기 질을 예측하는 머신 러닝 모델을 만들었다고 가정해 봅시다. 제 Python 동료는 Python 코드에서 내 모델을 사용하고 싶어합니다.
먼저 대기 질 예측이 어떻게 작동하는지 살펴보겠습니다. 세 가지 단계가 있습니다.
- .mat 파일에서 모델 로드
- openweathermap.org의 현재 날씨 데이터를 모델이 예상하는 형식으로 변환
- 모델의 predict 메서드를 호출하여 그 날의 예상 대기 질을 가져옵니다.
load airQualModel.mat model
testData = prepData(data);
airQuality = predict(model,testData)
airQuality =
Good
제 동료에게 이를 전달하기 위해 이러한 단계를 하나의 함수인 predictAirQuality로 묶어보겠습니다:
function airQual = predictAirQual(data)
% PREDICTAIRQUAL: 머신 러닝 모델을 기반으로 대기 질을 예측합니다.
%
%#function CompactClassificationEnsemble
% 데이터 유형 변환
currentData = prepData(data);
% 모델 로드
mdl = load("airQualModel.mat");
model = mdl.model;
% 대기 질 결정
airQual = predict(model,currentData);
% Python에서 사용하기 위한 데이터 유형 변환
airQual = char(airQual);
end
이 함수는 위에서 설명한 것과 같은 세 가지 단계를 수행합니다. 모델을 로드하고 데이터를 변환하며 모델의 예측 메서드를 호출합니다.
하지만 한 가지 더 해야 할 일이 있습니다. 모델은 MATLAB 범주 값을 반환하는데, 이는 Python에서 직접적인 등가물이 없기 때문에 문자 배열로 변환합니다.
이제 우리는 대기 질 예측 모델을 사용하는 MATLAB 함수를 가졌으므로, Python에서 이를 어떻게 사용하는지 살펴보겠습니다.